Cloud storage is offered in two models:
- Pay only for what you use
- Pay on a periodic or monthly basis
AWS (Amazon Web Service) owns more than 32 percent of the world’s public cloud services, followed by Microsoft Azure at 19%, Google at 7% and Alibaba Cloud, Digital Ocean and others. AWS serves more than 190 countries. One of its most powerful and commonly used storage services is Amazon S3. S3 (“Simple Storage Service”) it enables users to store and retrieve any amount of data at any time, provide developers access to highly scalable, reliable, fast, and inexpensive data storage. AWS claim that it provides 99.999999999 percent durability, AWS S3 also provides specific features for websites, mobile applications, backup and restore, and many other applications.
Let’s now see cloud storage in general.
What is AWS S3?
Amazon S3(“Simple Storage Service”) enables users to store and retrieve any amount of data at any time, place. According to AWS, S3 is designed for 99.999999999 percent durability
It can also store files up to 5 terabytes in size.
Benefits:
Let's see some of the benefits of the S3:
- Durable
- Availability
- Security
- Flexible
- Low cost
- Scalable
- High speed data transfer
Components of the AWS S3 cloud storage services
AWS Buckets and Objects
An object consists of data, key (assigned name), and metadata. A bucket is used to store objects. When data is added to a bucket, Amazon S3 creates a unique version ID and allocates it to the object.

Fig.1 Example of an object, bucket, and link address
Fig.2 Logging into AWS
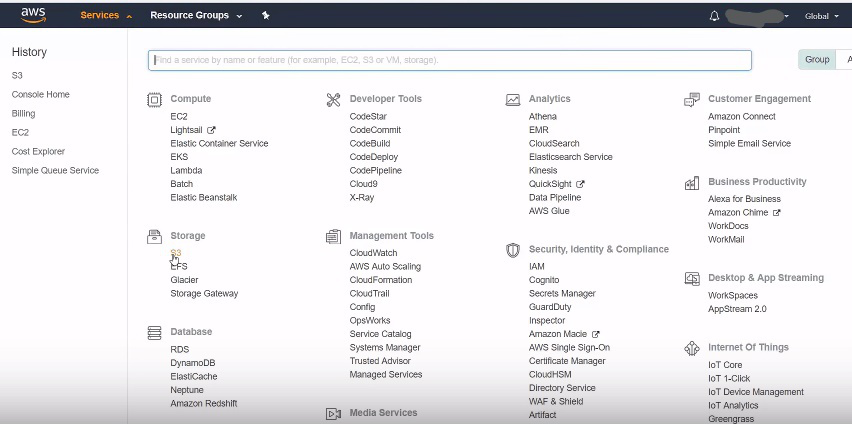
Fig.3 Search and select S3 from Service offerings
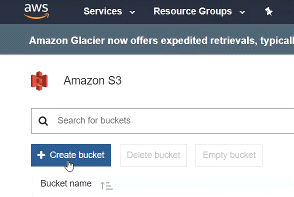
Fig.4 : Amazon S3 bucket list, create a bucket by clicking on the “Create bucket” button
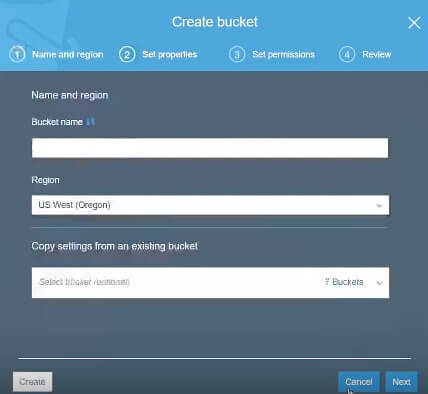
Fig.5 : Create a bucket by setting up name, region, and other options; finish off the process by pressing the “Create” button
3.Set permissions
Manage public permissions – Do not grant public read access to this bucket (Recommended)
Manage system permissions – Do not grant Amazon S3 Log Delivery group write access to this bucket
*Select the created bucket
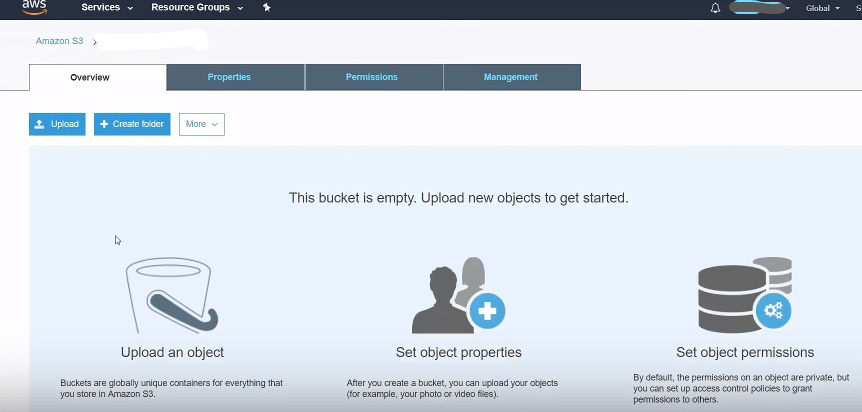
Fig.6 : Click on upload to select a file to be added to the bucket
*Select a file to be added
Let’s now look how we can automate this process by creating a simple in-depth AWS S3 with PHP integration guide.
Step 1:
First step first you need ACCESS KEY and SECRET ACCESS KEY for performing all S3 operation and performing operation in PHP SDK(used during CRUD operation).
NOTE: Use an access key ID and secret access key to authenticate an Amazon Web Services (AWS) account in a Cloud Storage migration project. An AWS secret access key can’t be retrieved after it has been created. Once lost, it cannot be recovered; a new access key must be created.Follow the steps below to create a new secret access key for an AWS account:
- 1. Sign in to the AWS Management Console and open the IAM console.
- 2. In the navigation pane, choose Users.
- 3. Add a checkmark next to the name of the desired user, and then choose User Actions from the top.
Click on Manage Access Keys:
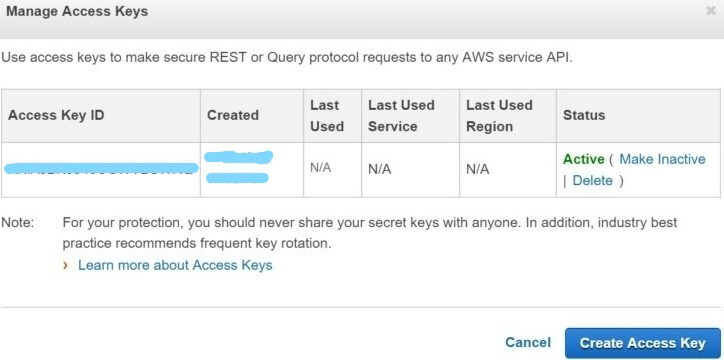
Note: Each AWS account can only have two access keys. If the secret access keys are lost, one of the existing access keys must be deleted, and a new one created.
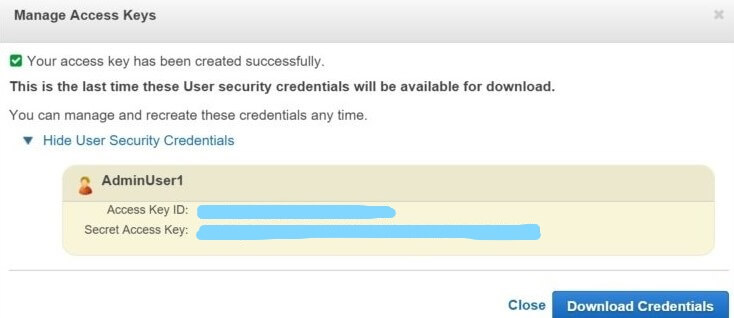
Manage Access Keys
- *Click on Show User Security Credentials.
- *Copy and paste the Access Key ID and Secret Access Key values, or click on Download Credentials to download the credentials in a CSV (file).
Step 2:
Installing the AWS SDK for PHP Version 3:
You can install the AWS SDK for PHP Version 3 by following ways:
- 1)As a dependency via Composer
- 2)As a ZIP file of the SDK
1)As a dependency via Composer:
*First thing you need to install Composer(Package manager for PHP) from this official website https://getcomposer.org/
*Visit to your project folder and then open terminal (Command prompt) and type command
composer require aws/aws-sdk-php
And now Add autoloader to your php scripts
To utilize the AWS SDK for PHP in your scripts, include the autoloader in your scripts, as follows.
require '/path/to/vendor/autoload.php'; ?>
2)Installing by Using the ZIP file:
The AWS SDK for PHP includes a ZIP file containing all the classes and dependencies you need to run the SDK. Additionally, the ZIP file includes a class autoloader for the AWS SDK for PHP and its dependencies.
To install the SDK, download the .zip file by clicking below link: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/aws-sdk-php/v3/download/aws.zip, and then extract it into your project at a location you choose. Then include the autoloader in your scripts, as follows.
require "/path/to/aws-autoloader.php";
Folder structure
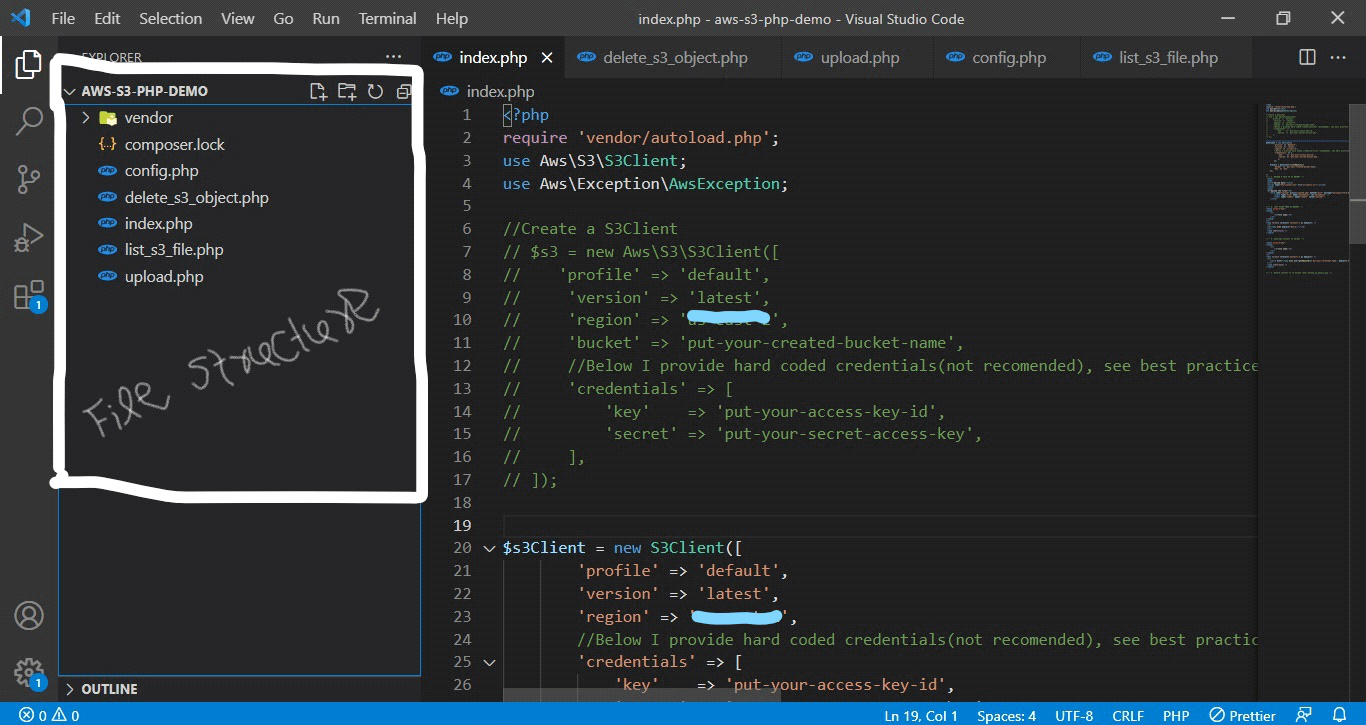
Now visit your INDEX.PHP(your main file where you write your script)
Creating a Client:
Write the below code to your file write as dependencies and initializer code:
require 'vendor/autoload.php';
use Aws\S3\S3Client;
use Aws\Exception\AwsException;
//Create a S3Client
$s3 = new S3Client([
'profile' => 'default',
'version' => 'latest',
'region' => 'us-east-2',
'bucket' => 'put-your-created-bucket-name',
//Below I provide hard coded credentials(not recommended), see best practice for providing credentials to your application https://docs.aws.amazon.com/sdk-for-php/v3/developer-guide/guide_credentials_hardcoded.html
'credentials' => [
'key' => 'put-your-access-key-id',
'secret' => 'put-your-secret-access-key',
],
]);
?>
Note: Way to provide credential:
*1) Use credentials from environment variables.Setting environment variables is useful if you’re doing development work on your local machine.
Using environment variables to contain your credentials prevents you from accidentally sharing your AWS secret access key. AWS S3 recommend that you never add your AWS access keys directly to the client in any production files. Many developers have had their account compromised by leaked keys.
To set environment variable in windows operating system:
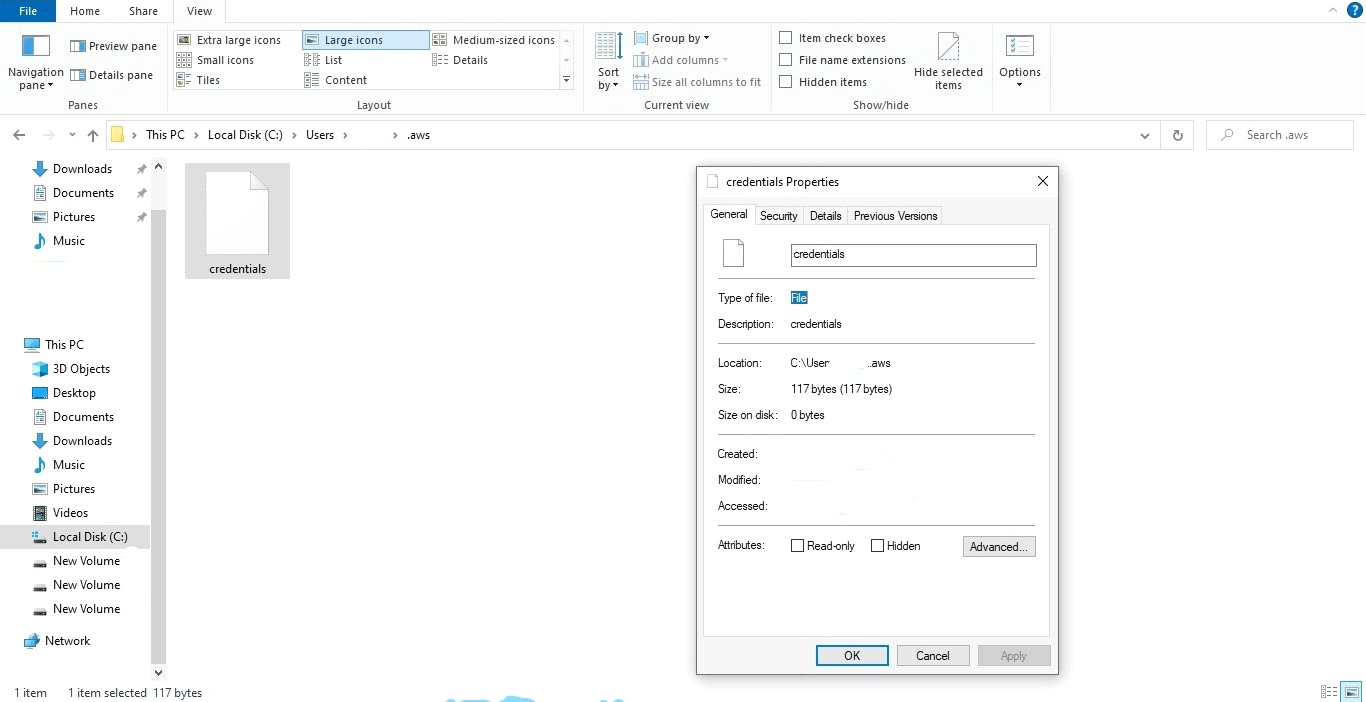 Visit to C:/ drive => Users => choose your root user(your computer user name like mike, john, mypc, win10 etc.) => create .aws folder =>inside create file name credentials (you can use Bracket editor for creating file)
Visit to C:/ drive => Users => choose your root user(your computer user name like mike, john, mypc, win10 etc.) => create .aws folder =>inside create file name credentials (you can use Bracket editor for creating file)
After creating file edit it and write below lines
[default]
aws_access_key_id = PUT_YOUR_AWS_S3_ACCESS_KEY
aws_secret_access_key = PUT_YOUR_AWS_S3_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY
AWS S3 PHP Integration operations:
1) Upload file to AWS S3 Bucket form (include this code in index.php file after the above code)
Note: *For uploading file putObject() method is used.For processing form of uploaded file create UPLOAD.PHP file and copy and paste below code
if(isset($_FILES['uploaduser'])){
$files = $_FILES['uploaduser'];
$name = $files['name'];
$tmpName = $files['tmp_name'];
$size = $files['size'];
$extension = explode('.', $files['name']);
$extension = strtolower(end($extension));
$key = md5(uniqid());
$tmp_file_name = "{$key}.{$extension}";
$tmp_file_path = "files/{$tmp_file_name}";
move_uploaded_file($tmpName, $tmp_file_path);
try{
$s3->putObject([
'Bucket' => 'put-your-created-bucket-name',
'Key' => "uploads/{$name}",
]);
//remove the file from local folder
unlink($tmp_file_path);
} catch (AwsS3ExceptionS3Exception $ex){
die("Error uploading the file to S3");
}
header("Location: index.php");
exit();
}
try{
$s3->putObject([
'Bucket' => 'put-your-created-bucket-name',
'Key' => "uploads/{$name}",
]);
*'Bucket' => 'put-your-created-bucket-name',
----> AWS S3 bucket name that you want to user as a source for
uploading your file.
*'Key' => "uploads/{$name}"
----> upload is folder name created inside AWS S3 bucket after you upload your file.
2) List all uploaded files from AWS S3 bucket:
3) Get download link of content inside AWS S3 bucket:
*Note: getObjectUrl() method used to get URL of files in your AWS S3 bucket
4) Delete content of AWS S3 bucket:
*Note: deleteObject() method used to delete files from your AWS S3 bucket
require('config.php');
$bucket = 'put-your-source-bucket-name'; //bucket name that contains your files/content
$folder ='aws-s3-folder-name-inside-your-file-store';
//like myfolder/
$keyname = 'file-name';
//like if your file name is flower.jpg then put this name in the place of keyname(that means the path of flower.jpg file is myfolder/flower.jpg)
$result = $s3->deleteObject([
'Bucket' => $bucket,
'Key' => $folder."/".$keyname
]);